The history of CNC machines
2022-01-12Machinery
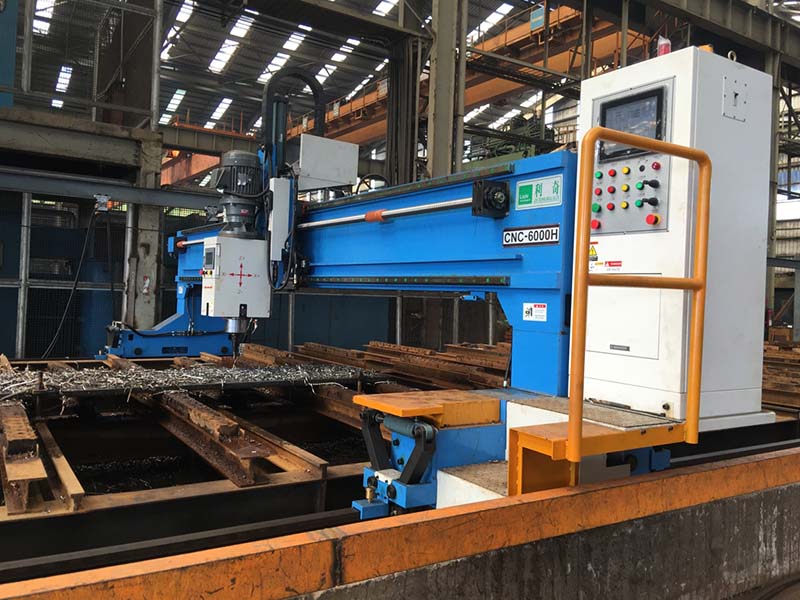

What is a CNC machine?
Generally speaking, a CNC machine is described as a machine tool operated automatically utilizing a computer system. When a CNC machine processes a piece of material, it may be made of any material such as metal, plastic, wood, ceramic, or composite. It does it automatically, without the need for a human operator.
The history of CNC gantry drilling machine:
CNC machines are electro-mechanical systems that operate machine shop tools in response to computer programming inputs. CNC is an abbreviation for Computer Numerical Control, which refers to.
It is one of two conventional ways (the other being 3D printing technology such as SLA, SLS/SLM, and FDM) for creating prototypes from a digital software file, the other being rapid prototyping. CNC gantry drilling machines can cut and treat a wide range of materials, including wood, metals, and plastics, for use in engineering and prototype firms, among other things.
Machines using computer numerical control (CNC) technology were created in the 1940s and 1950s, and they depended on a popular telecommunications data storage method called "punched tape" or "perforated paper tape."
Punched tape technology has been rendered obsolete since the 1950s and 1960s, as the data medium swiftly migrated to analog and then digital computer processing, respectively. The efficiency of CNC gantry drilling machines continues to increase as new technologies and higher levels of digital processing power are developed and implemented.
How does a CNC gantry drilling machine work?
In general, machining is transforming a stock piece of material, such as a block of plastic, into a completed product (usually a prototype component) by removing material from the stock piece under controlled conditions.
Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) and Computer-Aided Design (CAD) files, such as Solidworks 3D, are used to control CNC machines, which is similar to another prototype creation method called FDM (three-dimensional printing). While the CAM or CAD software does not drive the CNC machine, it does serve as a guide for the CNC to follow to produce the designs. The CNC machine interprets the design
The capacity to use computer devices to opera can significantly increase shop efficiency by automating highly technical and labor-intensive activities. Using automated cuts makes cutting prototype components more quickly and accurately, particularly when the material is important to the part's functionality.
Frequently, machining operations need several different tools to get the required results. CNC gantry drilling machines often combine tools into common units or cells, from which the machine may create its lines of cutting.
The movement of basic machines is limited to one or two axes. Still, the movement of sophisticated machines is limited to laterally in the x and y-axes, longitudinally in the z-axis, and often rotationally around one or more axes.
The ability to automatically turn components over on multi-axis machines allows you to remove material that was previously "underneath" the part. This removes the requirement for employees to flip the prototype stock material. It allows you to cut both sides of the prototype stock material without the need for human assistance.
Automated cuts are often more accurate than manual cuts since they do not need the user to intervene. Despite this, hand-finishing tasks like etching and basic cuts requiring substantial design work to train the machine for automation are sometimes preferable to automated methods.
Products
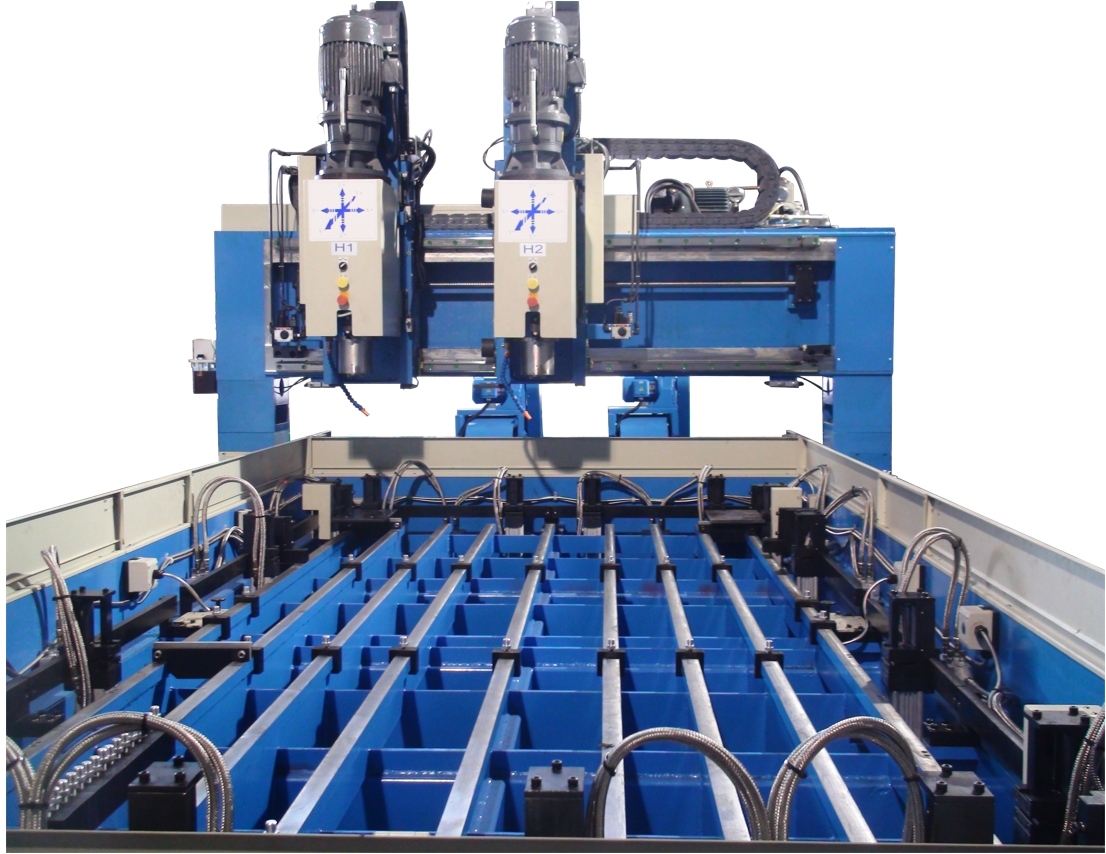

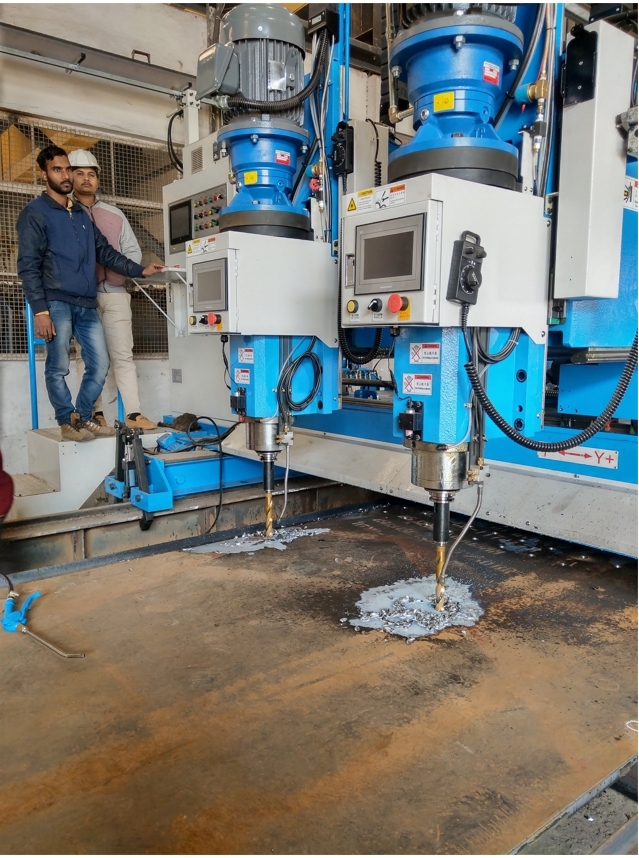
Plate Drilling Machine

Rail Type Bridge Plate Drilling Machine
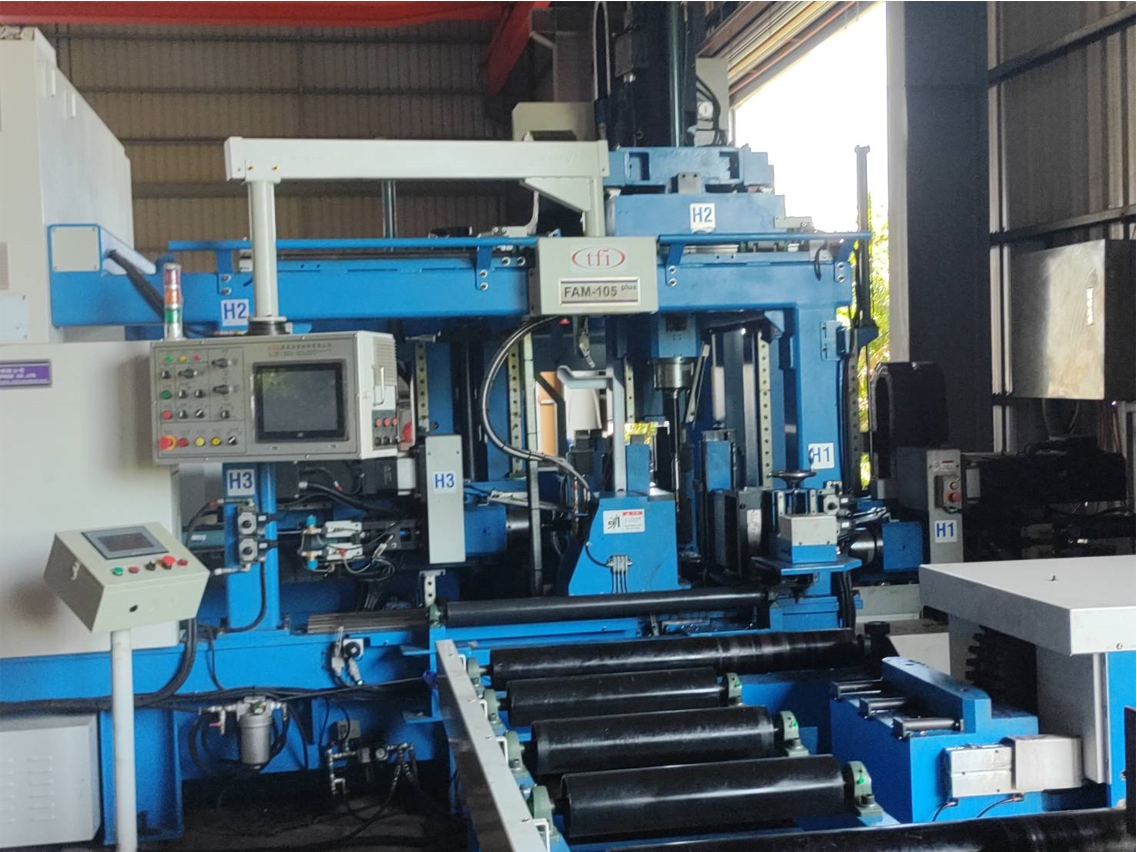

Beam Line Drilling Machine
Laser Marking Machine
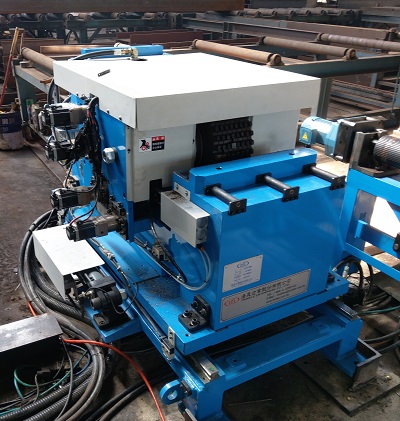

- H-Beam Bevelling machine
Products - Plate Drilling Machine
- Rail Type Bridge Plate Drilling Machine
- Beam Line Drilling Machine
- Laser Marking Machine
- Beam line stamper
- H-Beam Scallop & Beveling machine
- Plate beveling machine
- Auto Arm Welder
- Pipe Notcher
- Drill Grinder
- Magnetic Core Drilling Machine
- Remolift
- Shear Wrench
- H-Beam Rotater