What is a machine vise and its types?
2022-09-06Mould & Die From:HER BERT ENTERPRISE CO., LTD.
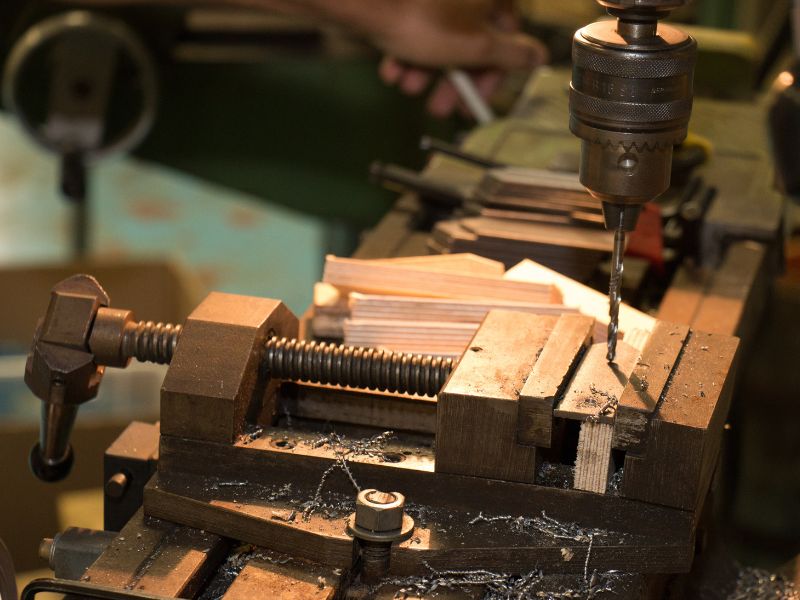

A machine vise — a mechanical gadget intended to keep workpieces as yet during machining tasks — can work as manual parts or as a machining gadget. Regular assembling offices use machining vises for applications that have tight resistances and require high accuracy.
A machine vise — a mechanical gadget intended to keep workpieces as yet during machining tasks — can work as manual parts or as a machining gadget. Regular assembling offices use machining vises for applications that have tight resistances and require high accuracy.
Typical machine vises are built from cast iron with replaceable steel jaws and are intended to hold a workpiece fixed during processing, drilling, forming, and grinding. A heavy-duty machine vise is recognized by its turn base and smooth jaws, whereas medium-duty machine vises include soft and one scored jaw.
Specific machine vises incorporate any-angle precision, ultra-accuracy, and self-centring machine vises.
A wide selection of machine vises is available, from the smallest to the largest. The light-duty vises serve as a general-purpose tool with a pedestal drill. Use a heavy-duty vise to steady a material while your machine it or drill a large hole into a hard material like steel.
Both machine vises will typically include a handle to aid in applying pressure while clamping down on the material.
After the machine vise's handle has been securely fastened by hand, additional force is applied with a mallet made of wood or hide (leather mallet).
The primary function of a machine vise is to secure large pieces of metal (steel, aluminium, etc.) during the machining process.
Underneath the material being machined is the pressing. This helps to stabilize the material and keeps it from shifting around during the machining process.
Types of machine vises:
• Plane Machine Vise
The plane machine vise is also called the light duty machine vise. The lightweight duty machine vise has been darted to the table of the drilling machine. This implies it is in the right position and won't move, even if the drill bit 'grabs' the work. Depending on the material being bored and the hole size, it is generally protected to hold the vise in hand (by the handle) and not essential to bolt it to the drilling table.
• Flange Machine Vise
Flange machine vises are heavy-duty machines with adjustable horizontal angles. The 'little' bolts are loosened, permitting the main body of the vise to turn 360 degrees on its horizontal axis. At the point when the ideal angle is reached, the bolts are fixed, standing firm on the point in position.
• Swivel Machine Vise
The swivel machine vise is built and shaped similarly to the flange machine vise, but it has a unique base that allows it to be rotated to any angle. Its benefit is that straight or precise machining should be possible without isolating the occupation from the vise.
• Universal Machine Vise
This is a highly helpful machine vise. The speciality of this machine vise is that it can be held in vertical, horizontal or angular positions. It is mainly used in the manufacture of devices.
• Vertical Machine Vise
This vise is unique to any remaining vise because these vise occupations are held vertically. Rather than jaws, here are flanges in this vise. With this vise of the can, he effectively held for machining.
To model and simulate the machine vise:
Objective:
1. To model the various parts of the machine vise.
2. To collect the parts.
3. To stimulate the machine vise from 0-10 seconds.
4. To plot a diagram between linear displacement and time.
Procedure:
1. Firstly, all the parts of the machine vise, right off the bat, are demonstrated utilizing Solidworks. Such as the fixed jaw, portable jaw, screw and handle.
2. All the parts are assembled accurately.
3. Presently the assembly is simulated for a period between 0-10 seconds.
4. From the recreation, a graph is plotted between linear displacement concerning time, and the outcome is considered.
Different types of Vises
Drill machine vise: A drill press vise is a gadget intended to get a workpiece immovably enough between its jaws that it won't move at all when the drill is squeezed into it. It's like other vises in that it utilizes a threaded rod to compel two jaws together.
G Clamp: G- clamps are a type of clamping device commonly used in carpentry and welding, among other trades.
Bench vise: A mechanical device known as a "bench vice" is used to secure an item for further processing. It highlights two parallel jaws as a part of the design.
Baby vise: A baby bench vise is a small, small-scale leisure activity vise with a connected table clamp which can be utilized to clamp the vise to the side of a table or work area. This cast-iron mechanical apparatus is used to tie down an item to permit work to be performed on it.
Bearing pullers: Its speciality device eliminates bearing from the armature shafts of compact power apparatuses like marble cutters.
Pipe vise: Plumbers use pipe vices to prevent lines or tubing from moving around while they are being threaded or cut. Pipes with a diameter of 3 mm can be held just as securely as those with a diameter of 200 mm.
Hacksaw Frames
A hacksaw frame is C-formed with a handle toward one side. The hacksaw edge stumbles into the open finish of the casing. Most hacksaw frame is 6, 10, or 12 inches in length.
Pros: This apparatus is precious, assuming the workpiece is little. A piece of metal is to be cut. The metal is fixed between the jaws of the vise firmly, and afterwards, it tends to be cut without any problem.
The vise holds the items to be dealt with firmly in a position. Thus, the hands of the laborer are allowed to work in the vise.
Cons: Very thin and delicate metals can't be hung on a vise. Assuming that it is a soft metal, the vise changes its aspect. It puts a few markings on the metal surface. Similarly, a workpiece of greater size can't be held in the vise.
FAQ
Why a machine vise is not suitable?
A machine vise is insufficient for holding sheet metal while drilling. The enlarged image shows the sheet metal bowing under the vise's pressure. If drilling continues, the dull tool will slip from its proper position, and the metal will almost certainly turn 'dangerously' out of the vise.